Parts of Speech Part 2
What's left? Let's review pronouns, prepositions, adverbs, and conjunctions and interjections!
:PRONOUNS:
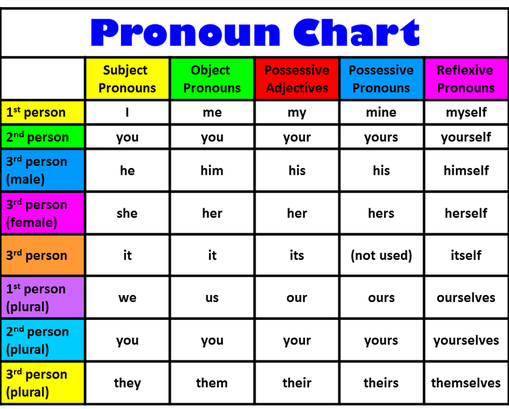
A pronoun is a word that is used in place of a noun.
Personal
Include subject pronouns, object pronouns, and possessive pronouns.
Subject
Used as the subject of a sentence. Subject pronouns are I, you, he, she, it, we, and they.
Used after an action verb or as the object of a prepositional phrase. Object pronouns include me, you, him, her, it, us, and them.
Takes the place of a possessive noun. Possessive pronouns include my, mine, your, yours, his, her, hers, its, our, ours, their, and theirs.
Refer to a single person or thing. They include I, me, my, mine, he, she, him, her, his, hers, it, its, and you. Use a singular pronoun with a singular verb.
Refer to more than one person or thing. They are we, us, our, ours, they, them, their, theirs, and you.
Point out nouns without naming them. They include this, that, these, and those.
Ask Questions. They include what, which, who, whom, and whose.
Emphasize the words they refer to. They include myself, himself, herself, yourself, itself, themselves, yourselves, and ourselves. the story.
Reflexive
Refer back to the subject of a sentence. The same pronouns that are intensive pronouns are also reflexive.
Personal
Include subject pronouns, object pronouns, and possessive pronouns.
Subject
Used as the subject of a sentence. Subject pronouns are I, you, he, she, it, we, and they.
- We were going to the zoo.
Used after an action verb or as the object of a prepositional phrase. Object pronouns include me, you, him, her, it, us, and them.
- Tim always calls me. (comes after action verb calls)
- Mary waved to him. (object of prepositional phrase to him)
Takes the place of a possessive noun. Possessive pronouns include my, mine, your, yours, his, her, hers, its, our, ours, their, and theirs.
- Her shirt is dirtier than mine.
Refer to a single person or thing. They include I, me, my, mine, he, she, him, her, his, hers, it, its, and you. Use a singular pronoun with a singular verb.
- Al's yard looked great after it was mowed. (Singular it replaces singular yard.)
Refer to more than one person or thing. They are we, us, our, ours, they, them, their, theirs, and you.
- Millie hung the pictures after they were dry. (Plural they replaces plural pictures.)
Point out nouns without naming them. They include this, that, these, and those.
- That is a great project!
Ask Questions. They include what, which, who, whom, and whose.
- Which can I take with me?
- I want to know who said that!
- Everything is packed in the car.
Emphasize the words they refer to. They include myself, himself, herself, yourself, itself, themselves, yourselves, and ourselves. the story.
Reflexive
Refer back to the subject of a sentence. The same pronouns that are intensive pronouns are also reflexive.
- Lucy surprised even herself.
Now, try taking this pronoun quiz:
http://grammar.ccc.commnet.edu/grammar/cgi-shl/quiz.pl/pronoun_quiz.htm
http://grammar.ccc.commnet.edu/grammar/cgi-shl/quiz.pl/pronoun_quiz.htm
:PREPOSITIONS:
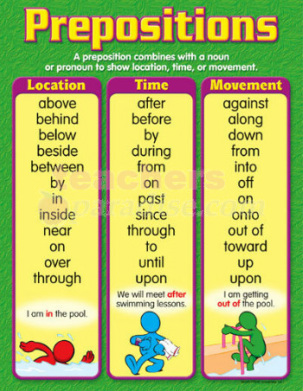
A preposition is a word or group of words that combines with a noun or pronoun to form a phrase that usually acts as an adverb, adjective, or noun. Prepositions can tell four things - location (where something is in relation to something else), direction (where something is going), time, and relationship (between a noun or pronoun and another word).
Examples:
TYPES OF PREPOSITIONS
Compound
Two or more words that work together like a one-word preposition. Some examples include according to, ahead of, along with, as for, instead of, except for, and in case of.
The noun or pronoun that follows a preposition in a prepositional phrase.
Examples:
- My dad stood outside the car. (location)
- My dad walked toward the car. (direction)
- My dad walked until 10:00 to wash the car. (time)
- My dad washed the car with Brian. (relationship)
TYPES OF PREPOSITIONS
Compound
Two or more words that work together like a one-word preposition. Some examples include according to, ahead of, along with, as for, instead of, except for, and in case of.
- Marilyn stood in front of me.
- Kelly sits near me.
- We went camping in spite of the terrible weather.
- Sue drove over the hill and around the forest.
The noun or pronoun that follows a preposition in a prepositional phrase.
- I put the money inside my coat pocket.
- The cat jumped out of the bag.
Click here to take a quiz on prepositions:
http://a4esl.org/q/f/z/zz98bck.htm
Try this game after the quiz:
http://www.manythings.org/vocabulary/games/k/words.php?f=prepositions
http://a4esl.org/q/f/z/zz98bck.htm
Try this game after the quiz:
http://www.manythings.org/vocabulary/games/k/words.php?f=prepositions
:ADVERBS:
An adverb is a word that describes a verb, an adjective, or another adverb.
Describes a Verb
Answers one of three questions: how? when? or where?
Doesn't' make a comparison.
Formed by adding er to one-syllable adverbs. Use more or less before most adverbs of more than one syllable.
Formed by adding est to one-syllable adverbs. Use most or least before most adverbs of more than one syllable.
Describes a Verb
Answers one of three questions: how? when? or where?
- The ballerina dances gracefully. (How does she dance? Gracefully.)
- The ballerina dances anywhere. (Where does she dance? Anywhere.)
- The ballerina dances daily. (When does she dance? Daily.)
- My dad is extremely tall. (How tall? Extremely.)
- My dog ran exceedingly quickly. (How quickly? Exceedingly quickly.)
Doesn't' make a comparison.
- Ann runs fast.
- Phil sings loudly.
Formed by adding er to one-syllable adverbs. Use more or less before most adverbs of more than one syllable.
- Ann runs fast, but Bill runs faster.
- Phil sings loudly, but Meg sings more loudly.
Formed by adding est to one-syllable adverbs. Use most or least before most adverbs of more than one syllable.
- Bill runs faster than Ann, but Rita runs fastest.
- Meg sings more loudly than Phil, but Guy sings most loudly.
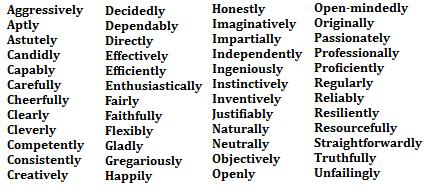
Here are some examples of adverbs:
Didn't like that one? Try this one:
http://www.oswego.org/ocsd-web/match/term/matchgeneric2.asp?filename=msmith5adverbmatch
http://www.oswego.org/ocsd-web/match/term/matchgeneric2.asp?filename=msmith5adverbmatch
:CONJUNCTIONS:
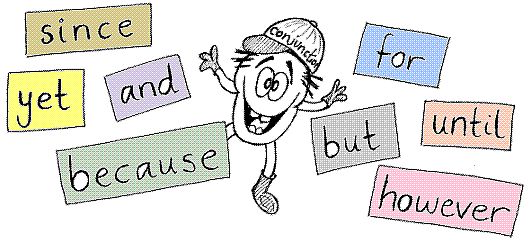
A conjunction connects words or groups of words together.
TYPES OF CONJUNCTIONS
Coordinating
Connect words, phrases, and sentences (independent clauses). Examples are and, nor, but, for, yet, so, and or.
Subordinating
Connect dependent clauses to independent clauses. Examples are after, before, so, till, where, although, for, so, that, unless, whereas, as, if, than, until, wherever, as if, once, that, when, whether, because, since, though, whenever, and while.
Correlative
Used in pairs that are split up by other words. Examples are either/or, both/or, neither/nor, not only/but also, just as/so, <and whether/or.
Adverbial
Connects clauses of equal value. Examples are accordingly, furthermore, consequently, moreover, hence, however, nevertheless, and therefore.
TYPES OF CONJUNCTIONS
Coordinating
Connect words, phrases, and sentences (independent clauses). Examples are and, nor, but, for, yet, so, and or.
- Megan bought apples and oranges for our lunch.
Subordinating
Connect dependent clauses to independent clauses. Examples are after, before, so, till, where, although, for, so, that, unless, whereas, as, if, than, until, wherever, as if, once, that, when, whether, because, since, though, whenever, and while.
- I won't go unless you apologize.
Correlative
Used in pairs that are split up by other words. Examples are either/or, both/or, neither/nor, not only/but also, just as/so, <and whether/or.
- Not only is it raining today, but it is also cold.
Adverbial
Connects clauses of equal value. Examples are accordingly, furthermore, consequently, moreover, hence, however, nevertheless, and therefore.
- I hate broccoli; however, I love cauliflower.
Click below to watch my favorite video about conjunctions EVER:
:INTERJECTIONS:
An interjection is a word or phrase that expresses strong feelings or emotions. It usually comes at the beginning of a sentence, followed by a comma or an exclamation mark.
- We won the race!
- I got an awesome present!
Still don't understand? Watch the video below:
Ready to test your skills?
Quiz 2
(on the bottom of this page, click continue for more exercises!)
http://web2.uvcs.uvic.ca/elc/studyzone/330/grammar/parts1.htm
(on the bottom of this page, click continue for more exercises!)
http://web2.uvcs.uvic.ca/elc/studyzone/330/grammar/parts1.htm
- CCSS.ELA-Literacy.L.3 Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking.
- CCSS.ELA-Literacy.L.3.1a Explain the function of nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs in general and their functions in particular sentences.
- CCSS.ELA-Literacy.L.3.1b Form and use regular and irregular plural nouns.
- CCSS.ELA-Literacy.L.3.1c Use abstract nouns (e.g., childhood).
- CCSS.ELA-Literacy.L.3.1d Form and use regular and irregular verbs.