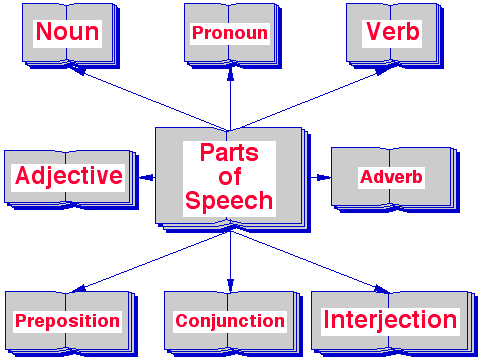
Parts of Speech
There is A LOT to cover on this page so TAKE YOUR TIME!
Students will learn parts of speech in American Standard English Language.
Before we begin, watch this video and introduce yourself to the different parts of speech:
Students will learn parts of speech in American Standard English Language.
Before we begin, watch this video and introduce yourself to the different parts of speech:
After watching the video, you should know there are EIGHT parts of speech: Pronoun, Adjective, Preposition, Adverb, Noun, Verb, Interjection, and Conjunction.
Let's quickly review what a noun, adjective, and verb:
:Noun:
A noun names a person, a place, a thing, or an idea. For example:
Common
Names a general person, place, thing, or idea. These nouns are not capitalized.
Abstract
Names an idea, feeling, emotion, or quality. fear, kindness, beauty
Collective
A noun that is singular in form but names a group of people, animals, or things. People, crew, audience, committee; Animals-herd, flock, litter; Things-collection, bundle, set
Singular
Names a single person, place, thing, or idea.book, bush, piano, leaf, ox
Plural
Names more than one person, place, thing, or idea. books, bushes, pianos, leaves, oxen
Adopted from https://sites.google.com/a/labrae.k12.oh.us/mrs-michele-deprofio-4th-grade-language-arts/writing/editing-marks/parts-of-speech
- Person (Jacob, girl, teacher, Mr. Singleton)
- Place (Chicago, school, Montana)
- Thing (computer, tree, elephant)
- Idea (happiness, anger, responsibility)
Common
Names a general person, place, thing, or idea. These nouns are not capitalized.
- building, holiday
- Names a specific person, place, thing, or idea. These nouns are always capitalized.
- Names something that you can see, touch, taste, hear, or smell.
Abstract
Names an idea, feeling, emotion, or quality. fear, kindness, beauty
Collective
A noun that is singular in form but names a group of people, animals, or things. People, crew, audience, committee; Animals-herd, flock, litter; Things-collection, bundle, set
Singular
Names a single person, place, thing, or idea.book, bush, piano, leaf, ox
Plural
Names more than one person, place, thing, or idea. books, bushes, pianos, leaves, oxen
Adopted from https://sites.google.com/a/labrae.k12.oh.us/mrs-michele-deprofio-4th-grade-language-arts/writing/editing-marks/parts-of-speech
:Verbs:
A verb is a word that describes action or a state of being. It is the main word in the predicate of a sentence.
Action
A word that describes a physical or mental action.
A linking verb says that something is, was, or will be. It does not show action.
Comes before the main verb. It helps state an action or show time. A main verb can have from one to three helping verbs. The helping verbs are <i>am, are, be, being, been, can, could, did, do , does, had, has, have, is, may, might, must, shall, should, was, were, will, would.
Is used when the subject of a sentence is singular.
Is used when the subject of a sentence is plural.
A verb is active if the subject of the sentence is doing the action.
A verb is passive if the subject is not doing the action.
Ends in ed when stating a past action or when using a helping verb. Most verbs in English are regular.
Does not end in ed when stating a past action or when using a helping verb.
Action
A word that describes a physical or mental action.
- The girl pointed to the correct letter.
- The teacher listened to the student's answer.
A linking verb says that something is, was, or will be. It does not show action.
- I will be the leader of my team.
- She is a student in my class.
- The food smells funny.
Comes before the main verb. It helps state an action or show time. A main verb can have from one to three helping verbs. The helping verbs are <i>am, are, be, being, been, can, could, did, do , does, had, has, have, is, may, might, must, shall, should, was, were, will, would.
- Janet was smiling at her new kitten.
- James has a test on Monday.
- I should have completed my project.
Is used when the subject of a sentence is singular.
- Samantha likes to write poems. (Samantha and likes are both singular.)
Is used when the subject of a sentence is plural.
- Some dogs eat bones. (Dogs and eat are both plural.)
A verb is active if the subject of the sentence is doing the action.
- Jack ran down the street. (The subject Jack is doing the action.)
A verb is passive if the subject is not doing the action.
- The project was made by Emma.(The subject project isn't doing the action.)
Ends in ed when stating a past action or when using a helping verb. Most verbs in English are regular.
- I cook.
- I cooked yesterday.
- I have cooked.
Does not end in ed when stating a past action or when using a helping verb.
- I write.
- I wrote yesterday.
- I have written.
:ADJECTIVES:
An adjective is a word that describes a noun or pronoun. An adjective usually answers one of three questions: What kind? How many? or Which one?
Demonstrative
Points out a noun. It always answer the question "Which one?" Demonstrative adjectives are this, that, these, and those.
Proper
Made from a proper noun and is always capitalized.
Positive
Describes a noun without comparing it to anything or anyone else.
Comparative
Compares two people, places, thing, or ideas.
Superlative
Compares three or more people, places, things, or ideas.
Demonstrative
Points out a noun. It always answer the question "Which one?" Demonstrative adjectives are this, that, these, and those.
- This dress is my favorite.
Proper
Made from a proper noun and is always capitalized.
- Lisa loves <b>Chinese</b> food. (from the proper noun China)
Positive
Describes a noun without comparing it to anything or anyone else.
- Our house is <b>big</b>.
Comparative
Compares two people, places, thing, or ideas.
- Our house is bigger than Jim's apartment.
Superlative
Compares three or more people, places, things, or ideas.
- Our house is the biggest house on the block.
OK, now that we have refreshed our memory, let's practice a little bit. Click here to play a game practicing what you have just learned about nouns and verbs.
http://www.missmaggie.org/scholastic/cleanup_eng_launcher.html
http://www.missmaggie.org/scholastic/cleanup_eng_launcher.html
Now, try either of these adjective games:
Now your ready to move on to part two of parts of speech! Good Luck!
- CCSS.ELA-Literacy.L.3 Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking.
- CCSS.ELA-Literacy.L.3.1a Explain the function of nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs in general and their functions in particular sentences.
- CCSS.ELA-Literacy.L.3.1b Form and use regular and irregular plural nouns.
- CCSS.ELA-Literacy.L.3.1c Use abstract nouns (e.g., childhood).
- CCSS.ELA-Literacy.L.3.1d Form and use regular and irregular verbs.